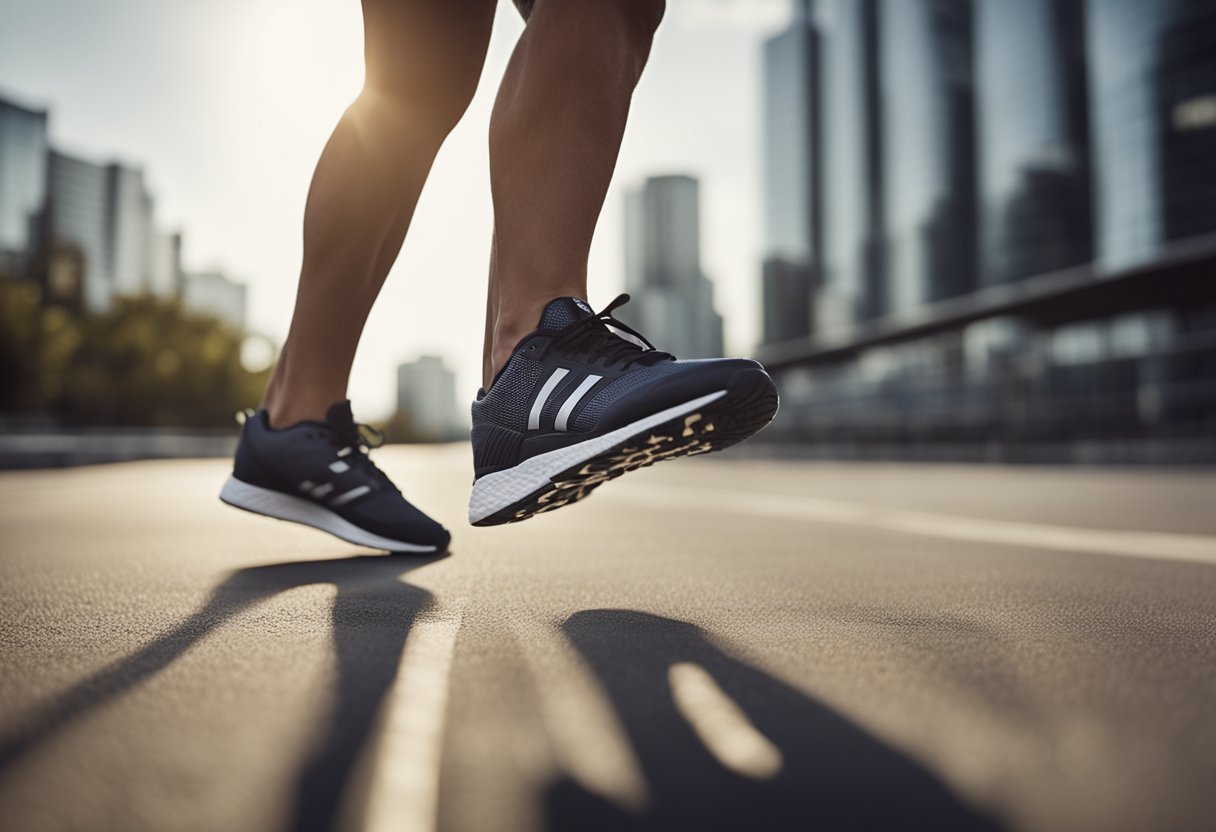
What is pronation? Pronation is an integral part of the human body and should be considered when working out or running.
If you are experiencing pain in your ankles, knees, hips, or lower back, it may be due to pronation.
Pronation is a natural movement when a foot lands while running or walking.
Composed of three cardinal plane components: subtalar eversion, ankle dorsiflexion, and forefoot abduction, these three distinct foot motions coincide during the pronation phase.
Pronation is a normal, desirable, and necessary component of the gait cycle. Pronation is the first half of the stance phase, whereas supination starts the propulsive phase as the heel lifts off the ground.
The foot’s normal biomechanics absorb and direct the occurring throughout the gait, whereas the foot is flexible (pronation) and rigid (supination) during different gait cycle phases.
As the foot is loaded, eversion of the subtalar joint, dorsiflexion of the ankle, and forefoot abduction occur. Pronation should not occur past the latter stages of midstance, as the standard foot should then supinate in preparation for toe-off.
Pronation is a term used to describe the natural motion of the foot during walking and running.
It is the inward rolling of the foot from the heel to the forefoot, which helps to distribute the body weight evenly across the foot.
Pronation is an ordinary and necessary movement that helps absorb shock and adapt to different surfaces.
Stages of pronation:
Underpronation – This type of supination needs a lot of cushioning to avoid impact injuries and additional stress on the feet.
Neutral pronation – a more natural moment of the foot’s movement. A wide shoe variety is available for this foot problem.
Foot pronation depends on a few factors, like how your foot contacts the ground.
If your heel touches the ground at an increased angle with slight or normal pronation, that causes robust transmission of the shock and stress on the leg.
Push-off is the pressure that goes on your smaller toes on the outside of the foot that can cause problems with balance.
Possible injuries are plantar fasciitis, shin splints, and ankle strain. A long list of other severe problems depends on the pronation type.
Determine your pronation type.
Pronation test – video gait analysis – this is an elementary test. The runner is on the treadmill like regular training, and the legs are filmed with a camera. Video footage is slowed down while watching and analyzed by a professional ASICS expert, a physical therapist, a podiatrist, or an expert from the sports industry running the store. An expert will determine the person’s running type to help pick the right shoes for the pronation type.
Expert guidance by ASICS store assistants – running stores have trained staff members who work with runners, joggers, and hikers, and they will help you find the right fitting shoes by providing individual shopping advice on shoes.
They can also help you diagnose your pronation type.
Wet feet test
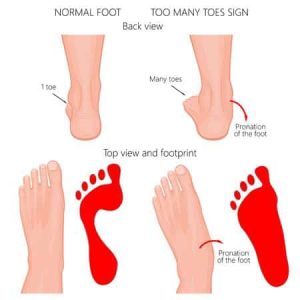
The foot arch test is a simple way to determine whether you have flat feet or high arches! Just follow these easy instructions: pour water into a shallow pan (the pan should be big enough to fit your foot, and the water should be just deep enough for all parts of the bottom of your foot to get wet); step into the water with one foot, then carefully remove your foot from the pan of water and step onto a flattened brown paper bag or piece of cardboard that will show your footprint (don’t just lightly place your foot onto the paper.
Be sure to put your weight on it!); remove your foot from the paper and take a photo for reference; repeat the process with your other foot.
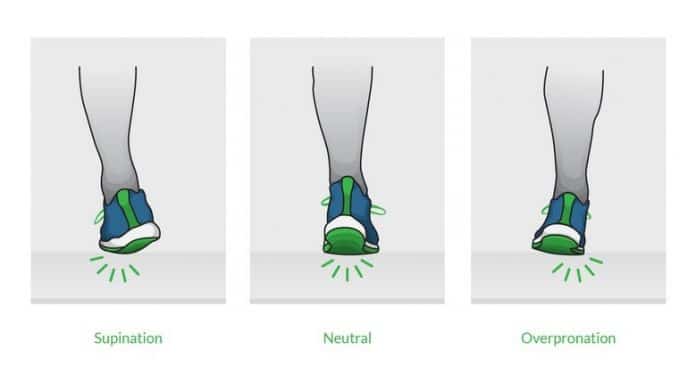
Simple pronation test by checking the wear pattern on your shoes
Determine under pronation (supination) – if you have this leg condition, the outside of your shoe will be almost worn out. Put your shoes on a flat surface, and you will notice a slight outward tilt on your shoes.
Determine the neutral pattern of walking – the soles of the neutral pattern walker shoes show an “S” shape from the outer heel in the significant toe direction. Neutral runner shoes will not show any tilt on a flat surface.
Determine overpronation – inside the heel and under the football will be extra worn out on the overpronators’ shoes. Inward tilt will be noticed on these shoes of overpronators.
Read Next – Best running shoes for neutral arches and supination.
How to choose the right shoes
When you have correctly diagnosed the pronation type of your feet, you can find proper shoe attire to help eliminate extra foot stress and lower the chance of injuries.
The right shoes will help get the body balanced and in a neutral posture, which will help the body arrange weight properly on the legs.
With a determined pronation type, you can find shoes with optimal cushioning and support in various designs that will fit your style.
Read Next – Top Cross Training Shoes for Pronation
Cushioned running shoes for the pronation feet type
Underpronators (supinators) tend to be susceptible to shock-related injuries, like fractures, and supinators need to find neutral running shoes with extra layers of cushioning of some new technologies like GEL cumulus cushion materials and foams.
Underpronation shoes focus on the midsole cushioning for extra shock absorption to lower possible injuries. Cushioning on the outer part of the shoes helps the foot counter the outward roll that supinators tend to have on the leg movement.
Exceptional cushioning is placed in the heel section to lower leg pressure. Flexible shoes that are soft enough help distribute impact while walking on the whole body.
Read Next – Shoes for supination.
Neutral running shoes for the neutral condition of the feet
Finding the correct shoes with standard pronation foot conditions is straightforward because the neutral movement can find different shoes. Specialized, neutral running shoes have extra cushioning and support, making walking even more accessible and balanced.
Gel Nimbus is the most famous manufacturer of cushioning materials for shoes. Cushioning in neutral runner shoes helps to promote natural foot motion.
Beginners at walking or running would like extra cushioning shoes for more support to help lower leg stress while muscles strengthen. Natural running shoes give more ground contact to the feet.
Read Next – Running Shoes for Supination Condition Features
Shoes for the Overpronation Condition of the Legs
Overpronators need most of the supportive shoes they can get. Overpronation needs extra support, layers of structured cushioning, and most of the support for stability. Gel Kayano is a leading manufacturer of structured cushioning shoes for overpronators.
Stability running shoes for the legs help distribute the impact of running on the legs to minimize pronation.
Medial post support is extra long and extends to the heel area. Flatter feet need a firm midsole for the arch support to position naturally. Overpronation can be severe, which is when motion-control shoes with extra cushioning are the best choice.
Read Next – What running shoes are best for supination?
However, excessive pronation can cause problems for the body. Overpronation is when the foot rolls too far inward, causing the arch to flatten and the ankle to turn inwards. This can stress the foot and leg muscles, leading to pain and discomfort. On the other hand, supination, also known as underpronation, is when the foot rolls outwards, putting pressure on the outer toes and causing problems for those with higher arches. Understanding pronation and how it affects the body is essential for maintaining proper foot health and preventing injuries.
Overall, pronation is a natural and necessary movement that plays a vital role in the body’s mechanics. However, understanding the different types of pronation and how they impact the body can help individuals maintain proper foot health and prevent injuries.
Understanding Pronation
Definition and Types
Pronation is a natural foot movement that occurs during walking or running. It is the inward rolling motion of the foot that helps to distribute the impact forces evenly. There are three types of pronation: neutral, over, and underpronation.
Neutral pronation is when the foot rolls naturally inward about 15 percent, allowing it to absorb the shock and keep the ankles and legs adequately aligned. This type of pronation is considered normal and healthy for the foot.
Overpronation occurs when the foot rolls inward excessively, causing the arch of the foot to collapse and the ankle to twist. This can lead to various foot problems, such as plantar fasciitis, shin splints, and knee pain.
Underpronation, also known as supination, is when the foot rolls outward, putting more pressure on the outside of the foot. This can lead to ankle sprains, stress fractures, and other foot injuries.
Biomechanics of Pronation
Pronation is a complex biomechanical process that involves the foot, ankle, heel, and arch. When the foot lands on the ground, it begins to roll inward, allowing the arch to flatten and absorb the impact shock. As the foot rolls inward, the ankle rotates inward, causing the lower leg to twist slightly.
This twisting motion helps to distribute the shock forces evenly throughout the foot and leg, reducing the risk of injury. As the foot pushes off the ground, it rolls outward again, returning to its neutral position.
Pronation vs. Supination
Pronation and supination are opposite movements of the foot. Pronation is the inward rolling motion of the foot, while supination is the outward rolling motion. Both movements are essential for normal foot function and gait.
Neutral pronation is the ideal foot movement for most people. However, some people may overpronate or underpronate, leading to foot problems. It is essential to wear shoes that provide proper support and cushioning for your foot type to prevent injuries.
Effects of Pronation on the Body
Pronation is a natural motion of the foot during walking and running. It involves the inward rolling of the foot as the arch flattens and the heel tilts inward. Pronation helps to absorb shock and adapt to uneven surfaces. However, excessive or abnormal pronation can lead to various problems in the lower limbs, gait, and posture.
Impact on Lower Limbs
Pronation affects the alignment and stability of the lower limbs, including the feet, ankles, knees, and hips. Overpronation, where the foot rolls inward too much, can cause the lower leg to rotate inward, leading to increased stress on the knee joint, which can cause pain and injury. Underpronation, where the foot rolls outward too much, can cause the lower leg to rotate outward, leading to increased stress on the ankle joint and the outside of the foot, which can cause pain and injury.
Influence on Gait and Posture
Pronation also affects the gait and posture of the body. Abnormal pronation can cause an uneven stride, leading to compensatory movements in other body parts, such as the hips and back. This can result in poor posture, muscle imbalances, and chronic pain.
Consequences of Abnormal Pronation
Abnormal pronation can lead to various injuries and conditions, such as plantar fasciitis, shin splints, and Achilles tendonitis. Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain and inflammation in the heel and arch of the foot. Shin splints are a common overuse injury that causes pain in the lower leg. Achilles tendonitis is a condition that causes pain and inflammation in the Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone.
In conclusion, pronation is a natural foot motion that helps absorb shock and adapt to uneven surfaces. However, excessive or abnormal pronation can lead to various problems in the lower limbs, gait, and posture, as well as injuries and conditions such as plantar fasciitis, shin splints, and Achilles tendonitis. It is essential to understand the effects of pronation on the body and to seek appropriate treatment if necessary.
Identifying Pronation Patterns
Pronation is a natural movement of the foot that occurs when the foot rolls inward after striking the ground. This movement helps to absorb shock and distribute impact forces evenly. However, excessive pronation can lead to various foot problems and injuries. Therefore, it is essential to identify your pronation patterns to choose the right shoes and prevent injuries.
Gait Analysis and Footprint Test
One way to identify your pronation pattern is to undergo a gait analysis. A gait analysis is a test that evaluates the way you walk or run. It involves observing your movements and measuring your stride, foot strike, and other factors. A gait analysis can help determine if you overpronate, underpronate, or have a neutral pronation.
Another way to identify your pronation pattern is to perform a footprint test. This test involves wetting your feet and stepping on paper or cardboard. The resulting footprint can show if you have a high arch (underpronation), normal arch (neutral pronation), or flat arch (overpronation).
Wear Patterns on Shoes
Another way to identify your pronation pattern is to examine the wear patterns on your shoes. Overpronators wear out the inside edges of their shoes, while underpronators wear out the outside edges. Neutral pronators wear out their shoes evenly. By examining the wear patterns on your shoes, you can determine your pronation pattern and choose the right shoes to support your feet.
It is important to note that wear patterns on shoes are not always accurate and should be used with other tests such as gait analysis and footprint tests. It is recommended to consult with a podiatrist or a running shoe specialist to get a professional opinion on your pronation pattern and the right shoes for you.
In summary, identifying your pronation pattern is crucial for choosing the right shoes and preventing injuries. Gait analysis, footprint test, and shoe wear patterns are some ways to identify your pronation pattern. It is recommended to consult with a professional to get an accurate assessment of your pronation pattern and the right shoes for you.
Choosing the Right Footwear
When choosing the proper footwear, it’s essential to consider your pronation type. Different pronation types require different shoes to provide the right support and cushioning to prevent injury and maximize performance.
Footwear for Different Pronation Types
For those with normal pronation, neutral running shoes with adequate cushioning are recommended. These shoes offer a balance of cushioning and support to help absorb shock and keep the feet in a neutral position.
People with overpronation, on the other hand, require motion-control shoes that offer maximum support and stability. These shoes are designed to reduce excessive inward rolling of the foot and provide additional arch support.
For those with underpronation, cushioned shoes with a neutral design are recommended. These shoes offer additional cushioning to absorb shock and support the outer edge of the foot.
Importance of Proper Cushioning and Support
The right cushioning and support are essential to prevent injury and improve performance. Shoes with inadequate cushioning can lead to injuries such as stress fractures, while shoes with inadequate support can lead to ankle sprains and other injuries.
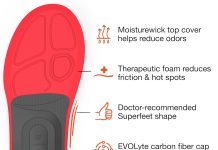
Orthotics can also be used to provide additional support and cushioning. Custom orthotics can be prescribed by a podiatrist or physical therapist to address specific foot issues and improve overall foot function.
Recommendations from Professionals
It’s essential to consult with a foot specialist or running store professional to determine the best type of shoe for your pronation type and foot shape. They can analyze your gait and foot shape to recommend the best type of shoe for your needs.
Choosing the right footwear is crucial for preventing injury and improving performance. By considering your pronation type, cushioning, and support needs and seeking professional advice, you can find the perfect shoe to keep your feet healthy and comfortable during exercise.
Managing and Preventing Pronation-Related Issues
Pronation is a natural movement of the foot that occurs when the foot rolls inward during walking or running. However, overpronation can lead to various foot and ankle problems, such as plantar fasciitis, shin splints, and Achilles tendonitis. Fortunately, there are several ways to manage and prevent pronation-related issues.
Exercises and Stretching
One way to prevent pronation-related issues is to perform exercises and stretches that strengthen the foot and ankle muscles. For example, calf raises can help strengthen the muscles, improving balance and stability. Another exercise is picking up marbles with the toes, which can help strengthen the foot arch.
Stretching is also essential to prevent pronation-related issues. Stretching the calf muscles can help reduce the strain on the Achilles tendon and plantar fascia. Additionally, stretching the plantar fascia can help reduce inflammation and pain.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy can be an effective treatment for pronation-related issues. A physical therapist can develop a customized treatment plan that includes exercises and stretches to strengthen the foot and ankle muscles. They can also use ultrasound therapy to reduce inflammation and pain.
Rehabilitation is also essential for managing pronation-related issues. Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) can help reduce inflammation and pain. Wearing supportive shoes and orthotics can also help reduce the strain on the foot and ankle.
When to Consider Surgery
In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to correct pronation-related issues. An orthopedic surgeon can perform procedures such as a tendon repair or ankle fusion to correct the foot and ankle alignment. However, surgery is usually considered a last resort after conservative treatments have failed.
In conclusion, managing and preventing pronation-related issues involves a combination of exercises, stretching, physical therapy, and rehabilitation. Surgery is only considered in severe cases when other treatments have failed. Individuals can maintain healthy feet and ankles by taking proactive steps to prevent pronation-related issues.
Pronation in Sports and Activities
Running and Pronation
Pronation is a natural foot movement that plays a crucial role in running. When a runner’s foot lands on the ground, it naturally rolls inward (pronates) to absorb shock and distribute the impact forces evenly. This movement helps to prevent injuries and provides stability and balance during running. However, excessive pronation can lead to overuse injuries such as shin splints, plantar fasciitis, and knee pain.
Runners with standard pronation patterns should wear neutral shoes with cushioning and support. Those with overpronation should wear motion-control shoes that provide extra support and stability. On the other hand, runners with supination (outward roll) should wear neutral shoes that provide flexibility and cushioning.
Other Activities Affected by Pronation
Pronation is not limited to running; it also affects other activities, such as walking and tennis. During walking, the foot naturally rolls inward to absorb shock, and excessive pronation can lead to foot and ankle pain. Tennis players must also pay attention to their pronation patterns, as excessive pronation can affect their balance and stability during lateral movements.
It is important to note that pronation is not necessarily wrong, as it is a natural movement of the foot. However, excessive pronation can lead to injuries and affect performance. Therefore, athletes must pay attention to their pronation patterns and wear appropriate shoes that provide support and stability.
In summary, pronation is a natural foot movement crucial in sports and activities such as running, walking, and tennis. Athletes should pay attention to their pronation patterns and wear appropriate shoes that provide support and stability to prevent injuries and improve performance.
Long-Term Health and Pronation
Pronation is a natural movement of the foot that occurs when the foot strikes the ground during walking or running. It is an integral part of the gait cycle, which helps to distribute the forces of impact across the foot and lower leg. However, excessive pronation can lead to various foot problems, including plantar fasciitis, shin splints, and knee pain.
Pronation in Aging Populations
As people age, their feet tend to become flatter, increasing the risk of overpronation. This is because the arches of the feet naturally begin to flatten over time, which can cause the foot to roll inward more than it should. This can lead to various foot problems, including bunions, hammertoes, and plantar fasciitis.
To help reduce the risk of overpronation in older adults, wearing supportive shoes with good arch support is important. This can help to reduce the strain on the foot and lower leg and may help to prevent foot problems from developing.
Lifestyle Factors Influencing Pronation
Several lifestyle factors can influence pronation, including obesity, pregnancy, and certain types of exercise. Obesity, for example, can increase the risk of overpronation, as the extra weight places additional strain on the foot and lower leg. Similarly, pregnancy can cause the feet to flatten and widen, increasing the risk of overpronation.
Certain types of exercise can also increase the risk of overpronation, particularly exercises that involve a lot of running or jumping. This is because these activities place a lot of stress on the foot and lower leg, which can cause the arches of the feet to collapse.
To help reduce the risk of overpronation, it is important to wear supportive shoes with good arch support and to avoid exercises that place a lot of stress on the foot and lower leg. Maintaining a healthy weight can also help reduce the risk of overpronation, particularly in older adults.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the effects of overpronation on the body?
Overpronation can lead to various problems, including pain and discomfort in the feet, ankles, knees, and hips. This is because overpronation causes the arch of the foot to collapse, which can result in poor alignment of the lower leg and knee. Over time, this misalignment can cause wear and tear on the joints, leading to conditions such as plantar fasciitis, shin splints, and IT band syndrome.
How can overpronation be corrected?
Overpronation can be corrected through various methods, including exercises to strengthen the muscles in the feet and legs, orthotics to provide additional support and alignment, and choosing appropriate footwear. Surgery may be necessary in some cases to correct severe overpronation cases.
What type of footwear is recommended for overpronation?
Regarding footwear for overpronation, choosing shoes that provide plenty of support and stability is essential. Look for shoes with a firm midsole, a sturdy heel counter, and a broad base to help distribute weight evenly across the foot. Motion control or stability shoes are often recommended for those with overpronation.
What is the difference between overpronation and underpronation?
While overpronation refers to the inward rolling of the foot, underpronation (also known as supination) is the opposite – the foot rolls outward. Underpronation can also cause problems with alignment and lead to conditions such as IT band syndrome and plantar fasciitis.
What are the indicators of an underpronated foot?
Indicators of an underpronated foot include high arches, calluses on the outer edge of the foot, and a tendency to wear down shoes on the outer edge. Those with underpronation may also experience pain in the ankle or foot.
Can pronation lead to other health issues?
Yes, overpronation can lead to various health issues beyond those related to the feet and legs. Poor alignment caused by overpronation can lead to issues with the spine and even affect the pelvis and lower back. It is essential to address overpronation to avoid long-term health issues.
Learn about Pronation and how to Prevent Pronation
Read also: The Best Running Shoes for Every Type of Run
Dr. Foot's 3/4 Length Orthotics Insoles - Best Insoles for Corrects Over-Pronation,Fallen Arches, Fat Feet - Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Bunions, and Other Foot Conditions (S - W7-8.5 | M5.5-7)
3/4 Insert Insole for Foot Pain from Plantar Fasciitis, High Arch,Flatfoot,Over-Pronation, Compound Orthopedic Arch Support Insole
SQHT Orthotics Medial & Lateral Heel Wedge Silicone Insoles for Supination and Pronation, Corrective Adhesive Gel Shoe Inserts for Bow Legs, Foot Alignment, Knock Knee Pain (Transparent+Brown+Black)
Orthotic Inserts 3/4 Length, High Arch Support Foot Insoles for Over-Pronation Plantar Fasciitis Flat Feet Heel Pain Relief Shoe Inserts for Running Sports Men & Women, M(Men's 7-10.5, Women's9-11.5)
$18.88 in stock
Rolyan Pronation & Supination Wheel, 2 Pound Weighted Wheel Training Device for Motor Control and Mobility, Hand & Arm Trainer for Forearm and Shoulder Surgery Recovery & Rehabilitation
High Arch Support Plantar Fasciitis Insoles Orthotic Inserts for Flat Feet and Over Pronation (M Women10.5-11.5 Men9.5-10.5)
PCSsole Orthotic Arch Support Shoe Inserts Insoles for Flat Feet,Feet Pain,Plantar Fasciitis,Insoles for Men and Women
$14.08 in stock
Powerstep Mens-Adult Pinnacle Shoe Inserts, BLUE, Men's 10-10.5, Women's 12
$38.99 in stock
2 used from $33.14
Pedag Pedag Correct Plus 3/4 Length Vegetable Tanned Leather Orthotic Footbed for Over-supinators, XLarge, (US Men 11-13)
Orthotic Inserts 3/4 Length, High Arch Support Foot Insoles for Over-Pronation Plantar Fasciitis Flat Feet Heel Pain Relief Shoe Inserts for Running Sports Men and Women, L|Men's 9-11, Women's 10-12
$18.88 in stock
Powerstep Unisex's Pinnacle Maxx Orthotic Insole Shoe Inserts, Workout Gear for Home Workou, Maroon, Men's 12-13 / Women's 14-15.5
$49.92 in stock
Vionic Unisex Full Length Active Orthotic Insole SupportMedium: Women's 8.5-10 / Men's 7.5-9
PCSsole Orthotic Arch Support Shoe Inserts Insoles for Flat Feet,Feet Pain,Plantar Fasciitis,Pronation For Men and Women
$14.32 in stock
Vionic Unisex Full-Length Supportive Relief Orthotic Shoe Insole - Comfort, Cushion, Arch Support, Heel Pain Relief, Plantar Fasciitis, X-Large (Men's Shoe Size: 11.5-13)
Powerstep Shoe Insole's Pinnacle Arch Support Orthotic Insert for Plantar Fasciitis, Equipment for Home Workouts, Blue, Men's 11-11.5, Women's 13-13.5
Read Next – How to Choose Running Shoes